27,53€
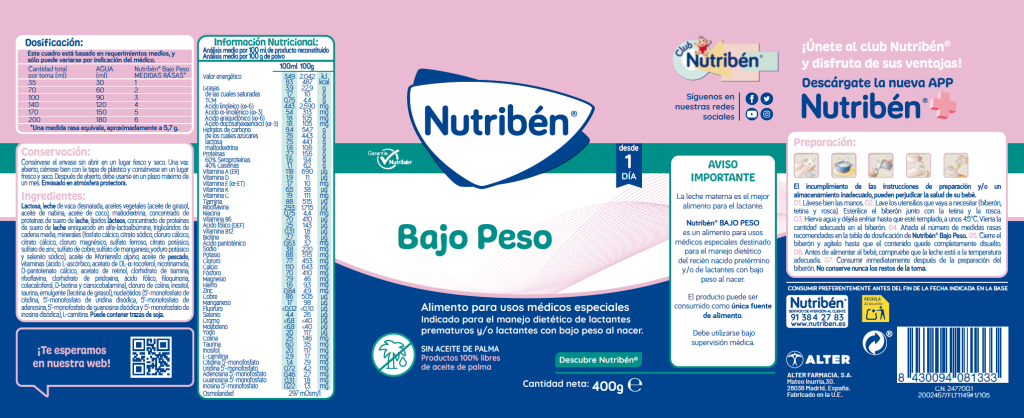
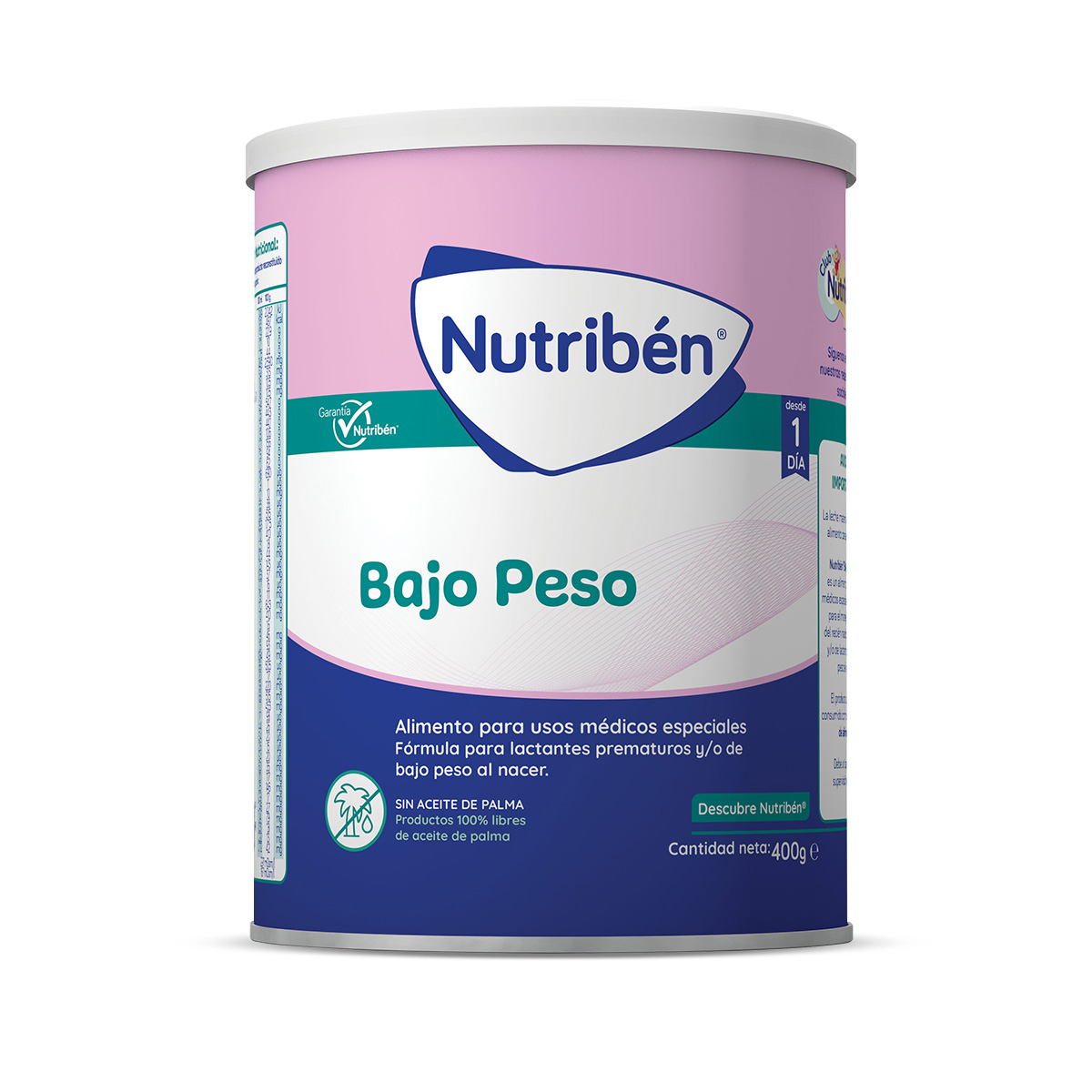
Nutribén recién nacido BAJO PESO es una leche de inicio para lactantes desde el primer día, indicada cuando la lactancia materna no es posible o es insuficiente. Nutribén R.N. Bajo Peso ha sido especialmente diseñada para cubrir las necesidades del recién nacido pretérmino y/o de lactantes con bajo peso al nacer. Debe seguirse el consejo del profesional de la salud competente.

La Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS*) ha recomendado que se informe a las mujeres embarazadas y a las que acaban de dar a luz de los beneficios y de la superioridad de la lactancia al seno, sobre todo que la lactancia materna es el medio ideal de nutrir a su bebé y de protegerle contra las enfermedades. Las madres deberían ser aconsejadas sobre la manera de prepararse a la lactancia al seno y a su mantenimiento, y sobre la importancia de una buena nutrición materna tanto durante el embarazo como después de dar a luz. Debería evitarse la introducción superflua de la alimentación parcial con biberón u otros alimentos y bebidas, debido a su efecto negativo sobre la lactancia. Asimismo, debería advertirse a las madres de la dificultad de desistirse después de haber decidido no iniciar o interrumpir la lactancia al seno.
Antes de utilizar una fórmula infantil, las madres deberían ser informadas de las consecuencias sociales y económicas de dicha decisión; por ejemplo, si el bebé está alimentado exclusivamente con biberón, necesitará más de una lata (450 g) por semana; así pues, hay que tener en cuenta la situación familiar y económica.
Habría que recordar a las madres que la leche materna no sólo es el mejor alimento para bebés sino que también es el más económico. Si se decide utilizar una fórmula infantil, es importante darles las instrucciones necesarias para su correcta utilización y llamarles la atención sobre el hecho de que el bebé puede enfermar si no se hierve el agua, no esteriliza el biberón o no se reconstituye el producto correctamente.
* Ver: Código internacional sobre la comercialización de los substitutos de la leche materna, adoptado por la Asamblea Mundial de la Salud en su Resolución AMS 34.22, Mayo 1981.
| Cantidad total por toma | Medidas rasas* | Agua hervida |
| 35 ml | 1 | 30 ml |
| 70 ml | 2 | 60 ml |
| 100 ml | 3 | 90 ml |
| 140 ml | 4 | 120 ml |
| 170 ml | 5 | 150 ml |
| 200 ml | 6 | 180 ml |
¿Consideras importante la Seguridad Alimentaria para tu bebé?
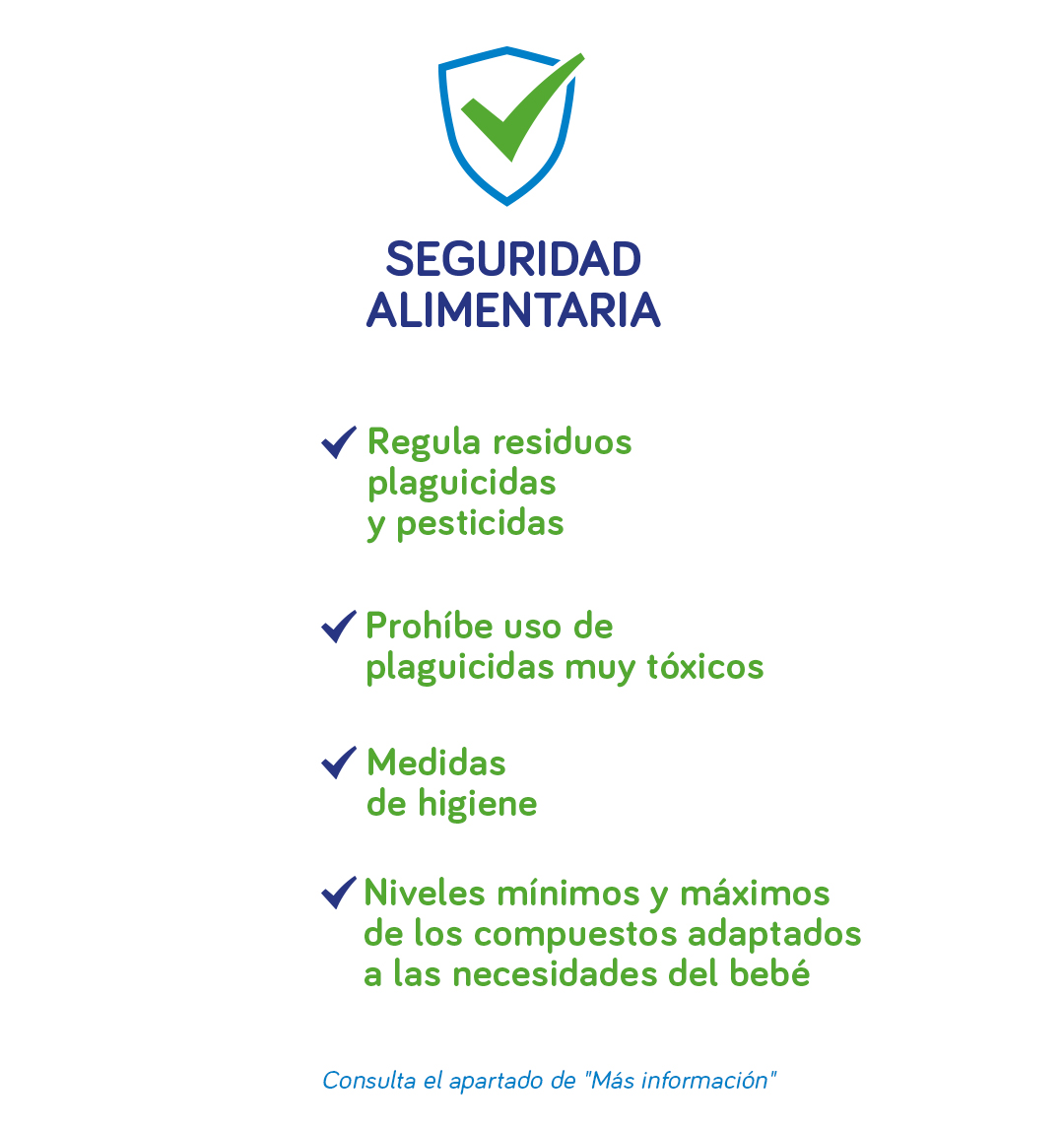
Los bebés hasta los 3 años son especialmente vulnerables a las bacterias. Por eso, cuando el destinatario de la alimentación es un bebé, la seguridad y calidad de los alimentos es mucho más importante.¿Sabes qué es la normativa Seguridad Alimentaria?
Es una normativa que aplica a la fabricación de los alimentos infantiles (0-3 años)- Regula la presencia de residuos de plaguicidas y pesticidas.
- Prohíbe el uso de determinados plaguicidas muy tóxicos para los bebés.
- Exige el cumplimiento de medidas de higiene, uso de aditivos alimentarios, contaminantes y el uso de materiales que vayan a entrar en contacto con los productos
- Define un nivel mínimo y máximo de todos los compuestos (energía, proteínas, carbohidratos, grasas, minerales, vitaminas y otros ingredientes), adaptados a las necesidades del bebé.
Principales diferencias entre la Seguridad Alimentaria para bebés y en alimentación general:
Los alimentos específicos para bebés cumplen con:- Requisitos mayores de calidad y seguridad.
- Límites más estrictos de metales pesados, micotoxinas, contaminantes químicos, residuos de plaguicidas...
- Sin aditivos colorantes y sin edulcorantes permitidos.
- Gran cantidad de nutrientes en pequeñas porciones de comida.













Simón Ichaicotó –
Buena iniciativa
Paola –
Me ha encantado, mi bebé nació prematura y comencé a darle está leche y ha subido de peso rápido. Ya ahora tiene 4 meses y está excelente de peso, pero no sé si debe comenzar con nuteiben natal o siga con la de bajo peso.